空间搜索-Lucene-Solr使用
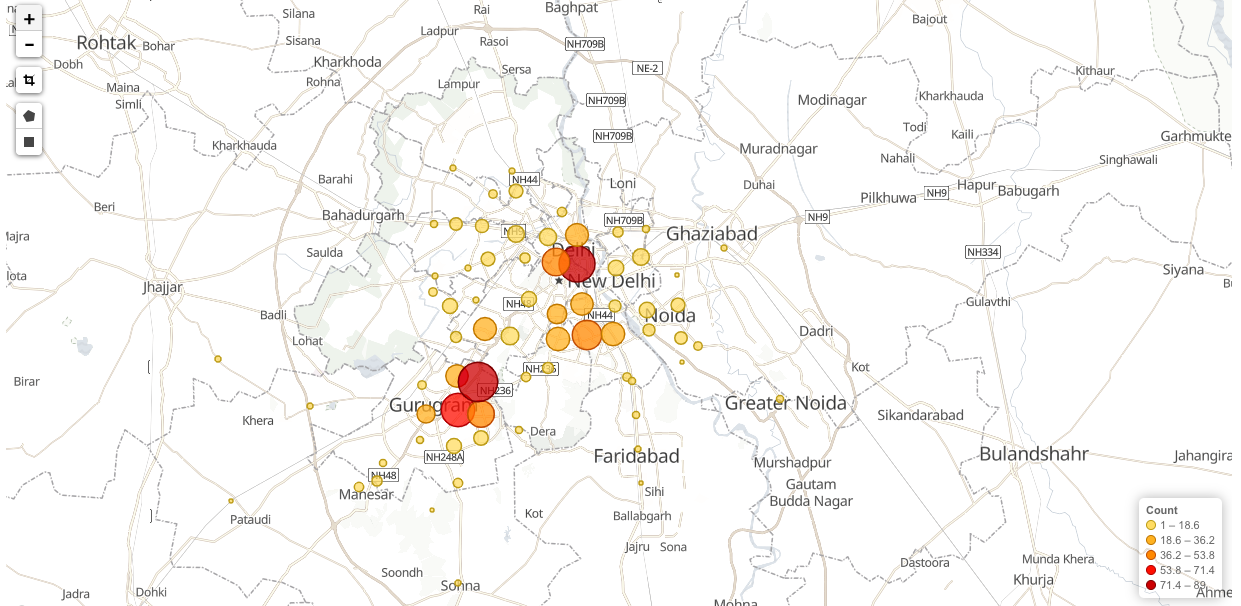
在Lucene-Solr中,提供了空间搜索能力,它主要提供了以下4种FieldType来支持:
LatLonPointSpatialFieldLatLonType(不再使用) , 以及非地理位置搜索版本PointTypeSpatialRecursivePrefixTreeFieldType(简写RPT), 包含衍生出的RptWithGeometrySpatialFieldBBoxField
LatLonPointSpatialField是用来取代LatLonType的一个FieldType。Lucene在7.0之后,推出了一种基于BKD树而实现的专用于处理多维数据的[索引格式,它原则上可以高效的处理任意维的数据。从一维的(int, long, double)数据类型、二维的点、面类型、三维的空间类型,甚至更多维度数据(暂未实现而已)。
1 | <fieldType name="location" class="solr.LatLonPointSpatialField" docValues="true"/> |
BBoxField是一种专门用来索引四方形数据的FieldType, 提供的功能包括:图形相交、图形内部、图形包含、图形相等。
1 | <field name="bbox" type="bbox" /> |
SpatialRecursivePrefixTreeFieldType则是最为通用的空间搜索解决方案。下面将对其重点来进行解释。
索引构建
定义空间索引类型和字段
在Solr中提供了scheme.xml文件用来定义索引类型和字段,如下所示:
1 | <fieldType name="location_rpt" |
对于重要的属性说明如下:
| 属性 | 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| name | location_rpt | fieldType名称,任意合法值 |
| class | solr.SpatialRecursivePrefixTreeFieldType | 用于深度遍历前缀树的FieldType,主要用于获得基于Lucene中的RecursivePrefixTreeStrategy。 |
| spatialContextFactory | JTS/Geo3D |
用来处理多边形定义和解析的类. 如果不填,则不能处理多边形数据。 |
| geo | true/false | true代表是地理数据。false则代表是正常的2D平面数据,采用Euclidean/Cartesian计算距离。 |
| format | WKT/GeoJSON |
默认是WKT |
| distanceUnits | degrees, kilometers , miles |
用来作为maxDistErr, distErr, d, geodist等的单位。当geo=true, 默认kilometers. 当geo=false, 默认是degrees. |
| distErrPct | 0.025 | 取值范围[0.0, 0.5]。用于进行精度控制。越低的值,精度越高,但速度越慢。默认值是0.025,通常不建议改。 |
| maxDistErr maxLevels | 0.000009 | maxDistErr定义为0.000009度,根据GeohashUtils.lookupHashLenForWidthHeight(0.000009, 0.000009)算出编码长度为11位,精度在1米左右 |
| worldBounds | 定义边界。默认是ENVELOP(minX, maxX, maxY, minY)。如果geo=true, 默认就是经纬度。否则需要自行指定。 | |
| distCalculator | 设置距离计算算法,geo=true默认是haversine,geo=false默认是cartesian(笛卡尔层),值可以为”lawOfCosines”(余弦定理), “vincentySphere”(文森特球面公式) 或 “cartesian^2” | |
| prefixTree | geohash/quad |
使用什么方案来网格化整个世界。geo=true时,默认使用geohash,否则使用quad |
| maxLevels | 索引网格的最大深度。优先级高于maxDistErr。通常11时,精度在1m左右,满足大部分需求。 |
其中prefixTree,可以用来指定使用geohash还是quad,分别对应于是GeohashPrefixTree类和QuadPrefixTree类,其中GeohashPrefixTree对应GeoHash算法,QuadPrefixTree对应Quad算法。
GeohashPrefixTree与QuadPrefixTree都继承SpatialPrefixTree这个前缀树基类,都使用了分层策略,主要索引和查询逻辑⼀样。不同点在于它们的maxLevels不一样,获取子cell的方式不一样,GeohashPrefixTree每层有32个子cell(编码base32),QuadPrefixTree 只有有4个子cell(笛卡尔分层)。
简单理解,geohash是一个32叉树,而quad是一个4叉树。
构建索引
构建索引代码示例(Point类型的索引):
1 | doc.setField(”poi_location_p", "32.52162,120.31778") //point类型 |
构建流程:
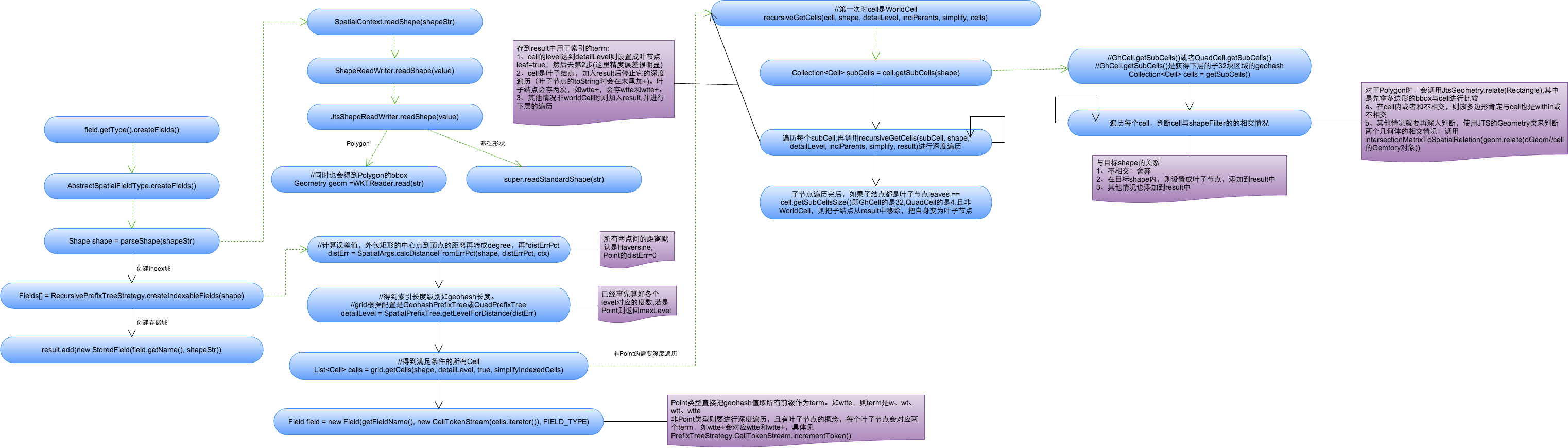
空间索引创建过程
下面主要说明Point类型的term创建过程。
1、将空间索引域的shapeStr解析成相应的Shape(这里指Point,复杂Shape如Polygon要使用JTS中的WTKReader来解析)。
2、创建索引域,具体过程参考org.apache.lucene.spatial.prefix.RecursivePrefixTreeStrategy中的createIndexableFields方法。
a、根据distErrPct字段,计算距离的误差值,对于Point来说默认为0(而对于非Point类型来说,是通过外包矩形中心点到矩形顶点的距离再乘以distErrPct来计算误差值的)
1 | double distErr = SpatialArgs.calcDistanceFromErrPct(shape, distErrPct, ctx); |
b、根据上述计算出的误差值,得到索引的geohash编码长度,对于Point类型来说值为maxLevels。
1 | public int getLevelForDistance(double dist) { |
c、根据编码长度得到满足所有条件的cells(每个cell表示一个前缀值),并将Cells都放在CellTokenStream中,同时构建索引域。Point类型每个Cell表示geohash的一个前缀值。
1 | public List<Cell> getCells(Point p, int detailLevel, boolean inclParents){ |
3、构建存取域存储索引
1 | if (field.stored()) { |
4、结果
如经纬度41.79452,123.41555,对应的geohash为wxrvb2kqexu(maxLevels=11), 则其对应的term有11个(如w、wx、wxr、wxrv…)。
查询
查询语法示例:
1 | q={!geofilt pt=45.15,-93.85 sfield=poi_location_p d=5 score=distance} |
涉及到的字段说明:
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| q | 查询条件,如 q=poi_id:134567 |
| fq | 过滤条件,如 fq=store_name:农业 |
| fl | 返回字段,如fl=poi_id,store_name |
| pt | 坐标点,如pt=54.729696,-98.525391 |
| d | 搜索半径,如 d=10表示10km范围内 |
| sfield | 指定坐标索引字段,如sfield=geo |
| defType | 指定查询类型 可以取 dismax和edismax,edismax支持boost函数相乘作用,dismax是通过累加方式计算最后的score. |
| qf | 指定权重字段:qf=store_name^10+poi_location_p^5 |
| score | 排序字段 根据qf定义的字段defType定义的方式计算得到score排序输出 |
其中有几种常见的Solr支持语法,其中有几种常见的Solr支持的几何操作:
- WITHIN:在内部
- CONTAINS:包含关系
- DISJOINT:不相交
- Intersects:相交(存在交集)
日常常见的需求主要分为2类:
1. 范围搜索(周边商家搜索)
范围搜索支持2种范围确定方式:
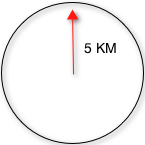
geofilt方式:根据搜索半径过滤结果,返回以pt为圆心d为半径的圆内所有点,如左图所示返回圆形内所有点
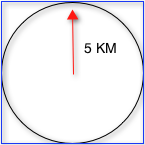
bbox方式:根据具体的域过滤结果,不仅返回以pt为圆心d为半径的圆内所有点,还包括域内其他点,返回矩形框内所有点,如下图所示:
范围搜索的情况很多,下面列举一些常用场景的查询语法:
不需要排序的场景
fq={!geofilt pt=45.15,-93.85 sfield=geo d=5}
fq={!bbox pt=45.15,-93.85 sfield=geo d=5}
需要排序的场景,较复杂
- 按距离排序,距离越近排名越高,加上score=distance,其中distance是索引点到坐标点之间的弧度值,系统根据弧度值排序。
1 | &fl=*,score&sort=score asc&q={!geofilt score=distance sfield=poi_location_p pt=54.729696,-98.525391 d=10}。 |
- 按距离排序,距离越远排名越高,加上score=reciDistance,其中reciDistance 范围是0~1 采用倒数的方式计算,故与distance的排序刚好相反
1 | &fl=*,score&sort=score asc&q={!geofilt score=reciDistance sfield=poi_location_p pt=54.729696,-98.525391 d=10} |
- 距离仅作排序不做过滤,在条件中设置filter=false,其中d只是确定形状的作用,不起限制作用。
1 | &fl=*,score&sort=score asc&q={!geofilt score=distance filter=false sfield=poi_location_p pt=54.729696,-98.525391 d=10} |
- 结合关键词查询和距离排序,此时关键字只能作为过滤条件(fq)不能作为查询条件,仅作为过滤域。
1 | &fl=*,score& fq=store_name:农业&sort=score asc&q={!geofilt score=distance sfield=poi_location_p pt=54.729696,-98.525391 d=10} |
- 当关键字和距离都作为排序条件时,可以用qf参数设置权重
1 | &fl=*,score& fq=store_name:农业&sort=score asc&q={!geofilt score=distance sfield=poi_location_p pt=54.729696,-98.525391 d=10} &defType=dismax&qf=store_name^10+poi_location_p^5 |
2.图形搜索
- 直线附近1km商家搜索
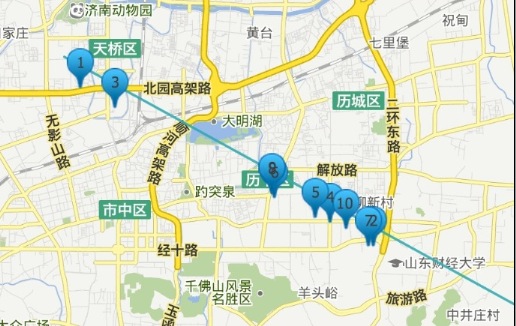
1 | &fl=*,score&sort=score asc&q=poi_location_p:"Intersects(LINESTRING(116.38263702392578 39.86653357724533,116.4935302734375 39.8578370694061) d=1 |
- 正常多边形范围内的商家
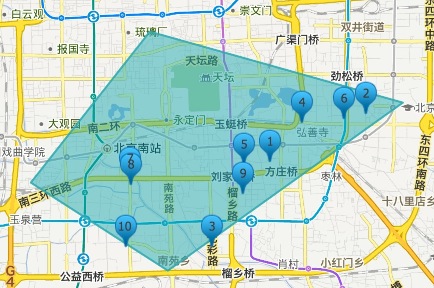
1 | &fl=*,score&sort=score asc&q=poi_location_p:"Intersects(POLYGON ((116.37714385986328 39.88392328618825,116.46709442138672 39.86627006289872,116.40392303466797 39.83358644035512,116.33525848388672 39.85124807212413,116.37714385986328 39.88392328618825))) distErrPct=0 |
3)复杂(如自相交)多边形范围内的商家
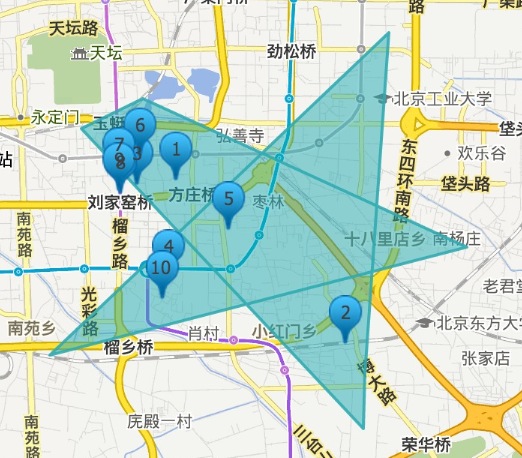
b 对于这种自相交的多边形,Solr默认认为是非法的,会抛出类似这样的异常: com.spatial4j.core.exception.InvalidShapeException: Self-intersection at or near point (116.4272689819336 39.875755941712825, NaN),因此在将参数传入solr前,需要基于标准 Douglas-Peucker Algorithm 算法对多边形进行处理,处理后能去掉自相交的部分,效果如示意图所示:
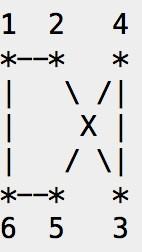
处理后,自相交的部分变为3和6两个点。当然经过处理后的多边形数据会损失一些精确度。
简化前:
1 | POLYGON((116.4272689819336 39.875755941712825,116.50142669677734 39.84966661865515,116.4059829711914 39.83068633533497,116.48357391357422 39.8873480121113,116.47808074951172 39.827258780634594,116.47773742675781 39.8177661982179,116.41319274902344 39.87048617098581,116.4272689819336 39.875755941712825)) |
简化后:
1 | POLYGON ((116.4272689819336 39.875755941712825,116.45455487823865 39.866156528285366, 116.48357391357422 39.8873480121113, 116.48079281261445 39.85692579689432,116.50142669677734 39.84966661865515,116.47973485573046 39.84535290095104,116.47808074951172 39.827258780634594,116.47773742675781 39.8177661982179,116.45096720829837 39.8396320628827,116.4059829711914 39.83068633533497,116.43551562011505 39.85225289138226,116.41319274902344 39.87048617098581,116.4272689819336 39.875755941712825)) |
简化后查询语法变为:
1 | &fl=*,score&sort=score asc&q=poi_location_p:"Intersects(POLYGON ((116.4272689819336 39.875755941712825,116.45455487823865 39.866156528285366, 116.48357391357422 39.8873480121113, 116.48079281261445 39.85692579689432,116.50142669677734 39.84966661865515,116.47973485573046 39.84535290095104,116.47808074951172 39.827258780634594,116.47773742675781 39.8177661982179,116.45096720829837 39.8396320628827,116.4059829711914 39.83068633533497,116.43551562011505 39.85225289138226,116.41319274902344 39.87048617098581,116.4272689819336 39.875755941712825)) distErrPct=0 |
无论是范围查询还是图形搜索,他们的查询基本流程都类似,主要分为下面2步:
1、解析查询,生成Query树:获得相应的QParse(SpatialFilterQParser),对查询串进行语法解析,获得查询串的各个参数,并且获得相应的查询Query(包括相应的Filter),其中也计算了查询Shape的一些属性,如最大索引长度detailLevel。
1 | Query result = null; |
2、查询:SolrIndexSearch.search()进行创建Weight树和Score树,利用不同的filter和score策略得到符合条件的docIdSet。而对于几种不同的几何图形关系,Solr提供了几种不同的filter类来计算,这些filter都继承AbstractPrefixTreeFilter类,简单来说就是获取与查询Shape相交的所有子Cell,然后再与term进行匹配的过程。
参考文档:
https://tech.meituan.com/2014/09/02/solr-spatial-search.html